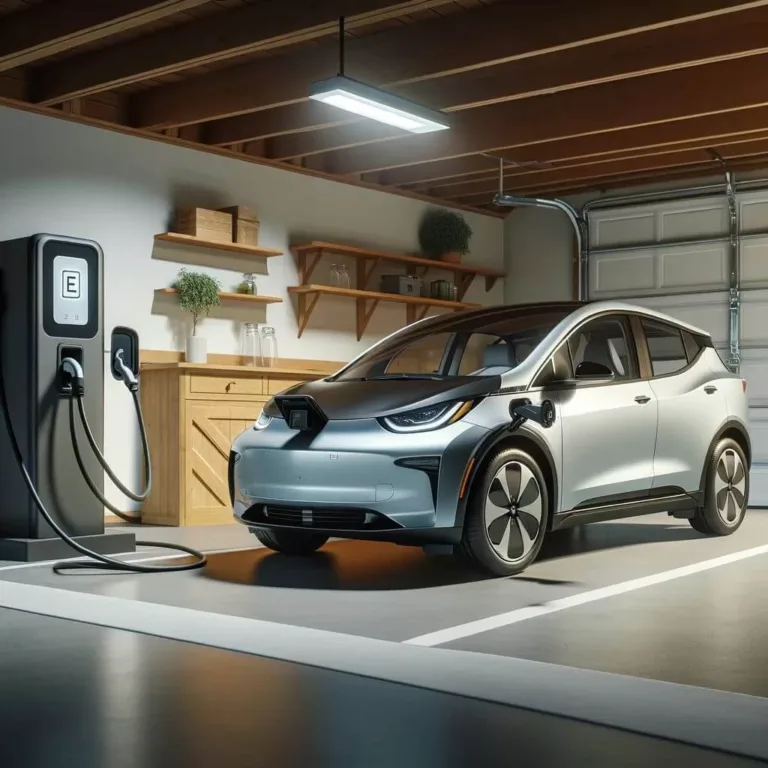
Your EV Charging Solution Specialists
Main Line Charging is a Licensed and Insured Electrical Contractor based in the heart of the Philadelphia Main Line, servicing Delaware, Montgomery, and Chester Counties.
Services We Offer
Catering to Your Charging Needs: Our Comprehensive EV Charging Solutions
Installation of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
- Single family homes
- Multi-family homes (apartments and condos)
- Commercial locations
- Supermarkets
- Restaurants
- Parking lots
- Office campus
- Country clubs and more
Upgrades and Repair
- Residential and commercial Electrical Service and Electrical Panels
Installation
- New Residential Construction
- Residential Additions
- Tamper Resistant Outlets, GFCI outlets
- Ceiling Fan Installation
- Landscape Lighting, Recessed Lighting
- Commercial Installation and Repairs
- Dedicated Circuits
Electrical Safety Inspections
Request a EV Installation
About EV Chargers
Most drivers will recharge their vehicles at home each evening, so before you invest in a Battery Electrical Vehicle (BEV), there are a few things you should know, and understand about charging and the different types of chargers.
Owners should be aware that there is a charging cycle. Therefore it usually takes longer to recharge the last 5-10% of the battery than the first 90%. This is due to the charger reducing the power flow to a trickle charge so as to not overcharge or damage the battery.
Also owners should be aware that many Electric Vehicles are currently limited in how much power they can draw from a charging station, this extends the time it takes to get a full charge. Many manufacturers such as GM recognize this choke point and are currently building their vehicles to be able to accept higher levels of power from different levels of chargers.
Here are the key differences between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 (also known a DC Fast Charging).
Level 1 chargers come standard with most electric vehicles and are generally sold with the vehicle. This charger can be plugged into any normal three-prong outlet. On the plus side Level 1 chargers require no additional electrical installation, and are great for emergency backup when traveling, however it charges the vehicle batteries extremely slowly.
A level 1 charger is best suited for overnight use or short range travel (30 to 40 mile per day). However if the battery is fully depleted it can take up to 24 hours or more to fully charge. Charging rates are around 3.5 – 6.5 miles of driving range per hour of charging time.
Level 1 charging can also ideal for plug-in hybrid electric cars that have smaller batteries
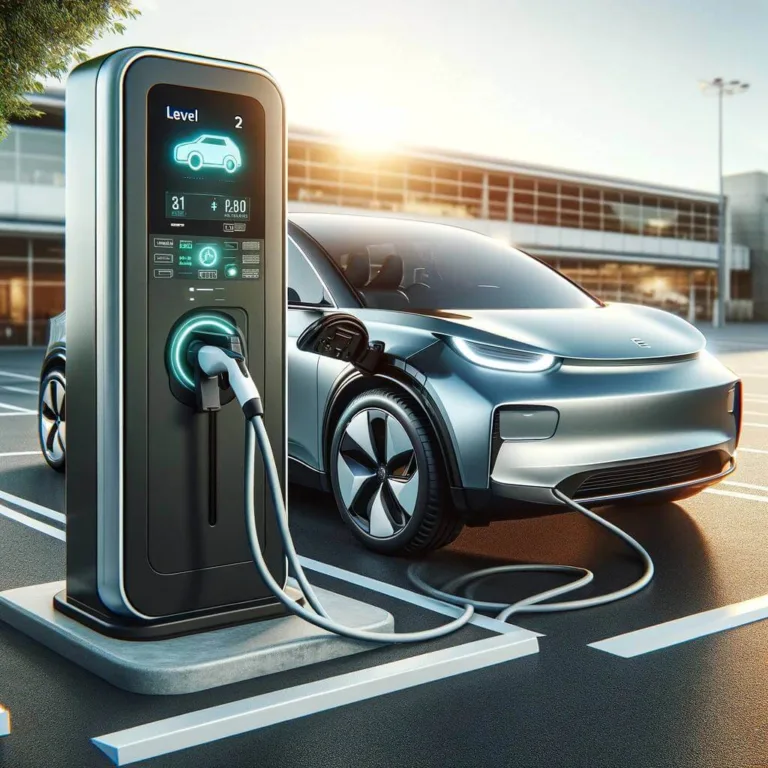
Level 2 charging is considerably faster than Level 1, but requires installation of a charging station, also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). Charging station installation requires a dedicated 240-volt or 208-volt electrical circuit, similar to what is required for a clothes dryer or electric r
Level 2 charging is considerably faster than Level 1, but requires the installation of a charging station, also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE).
A Charging station installation requires a dedicated 240-volt or 208-volt electrical circuit, similar to what is required for a clothes dryer or electric range.
Level 2 chargers are typically found at public and workplace charging stations, and they are becoming increasing common in residential homes.
These chargers use the same standard connector as Level 1 chargers, meaning any electric car can plug in at any Level 2 charge; however, the amount of kWs the vehicle will draw from the charging station will depend on the vehicle manufacturers design. As a general rule, older EV models will tend to draw lower amounts of power than newer models.
Depending on the battery type, charger configuration and circuit capacity, the fastest Level 2 charging unit (at 19.2kW rating) can add about 60-70 miles of range per hour of charge time, with the average Level 2 (at 9.6kW rating) generating 20-30 miles of range per hour of charging time.
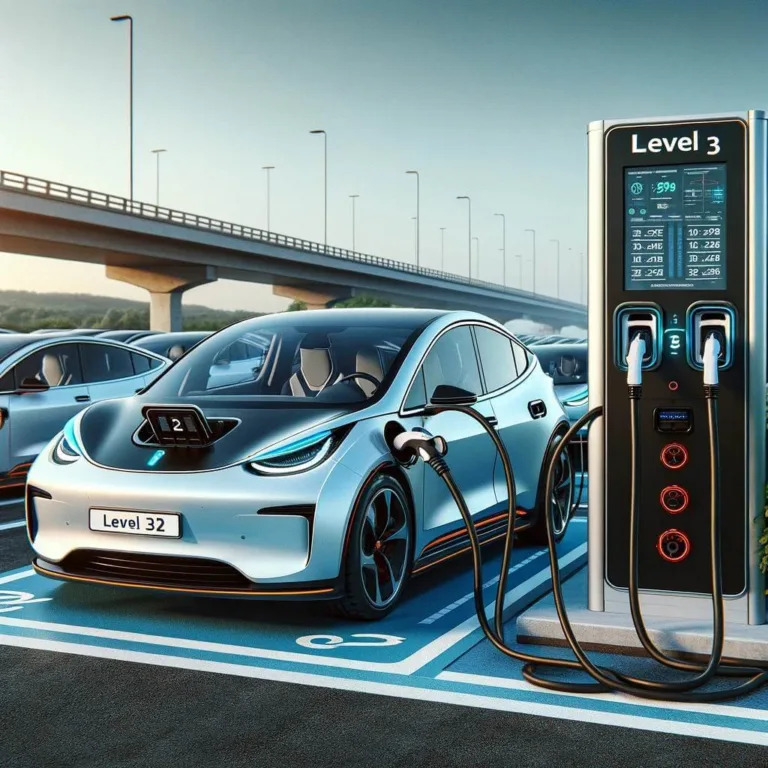
These are standalone devices seen mostly at highway rest stops and public charging stations in shopping centers.. It can fully recharge many EV’s batteries in about 30 minutes. Depending on battery type, charger configuration and circuit capacity, DC fast charging can add up to 10-15 miles of range per minute of charging time.
DC fast charging provides the fastest available recharge. They require a 480-volt connection, and as such DC fast charging is unsuitable for home use. Many older EV’s are not equipped to handle the higher power available. However, newer models are all designed for these faster charging platforms.
There are 3 different types of DC fast chargers
- CHAdeMO;
Combined - Charging System (Combo or CCS); or,
- Tesla connector system.
Level 3 chargers range from the more common 50kW chargers up to the currently very rare 350kW chargers.
Request a EV Installation
EV Charging Cost Considerations
There are several options to recharge an EV.
Most drivers will recharge their vehicles at home each evening, so before you invest in a Battery Electrical Vehicle (BEV), there are a few things you should know, and understand about charging and the different types of chargers.
Owners should be aware that there is a charging cycle. Therefore it usually takes longer to recharge the last 5-10% of the battery than the first 90%. This is due to the charger reducing the power flow to a trickle charge so as to not overcharge or damage the battery.
Also owners should be aware that many Electric Vehicles are currently limited in how much power they can draw from a charging station, this extends the time it takes to get a full charge. Many manufacturers such as GM recognize this choke point and are currently building their vehicles to be able to accept higher levels of power from different levels of chargers.
Most houses have a 240Volt panel. Panel capacity varies from smaller 100Amp up to 400Amp. Depending on the current load, a dedicated EV charging circuit may require upgrade of the electrical panel, meter socket and service entrance cable. Upgrade of the electrical panel will obviously increase the cost of installation of an EV charging station.
Some charger manufacturers such as Tesla also plan to allow “load sharing”. Load Sharing is when the load is balanced between several charging stations, to ensure multiple vehicles can share the maximum power available on a single EV charging circuit. This alternative should be considered by all multi car households, as it allows several vehicles to be connected to the same circuit, so it may not be necessary to upgrade electrical panels or service if there are multiple EV vehicles plugged in at the same time.
Many employers provide charging facilities as a benefit for their employees to utilize while they are at work. If you would like us to contact your if your employer to determine if they would be interested in hosting a station, please click here to send us an email.
Many people charge their electric car at public charging stations. They can be free, pay-as-you-go or subscription-based, with prices set by networks or property owners. Some automakers, such as Hyundai, Nissan and Tesla may provide complimentary charging at certain public chargers. It should be noted that the industry is moving toward a fee structure based on kWh used, rather than by the time it takes to charge the car.
Drivers in Pennsylvania may expect to pay around 30 cents per kWh to charge on Public Level 2, and 40 cents per kWh for Public Level 3 (DC fast charging). At these rates, an EV with 330-mile range and 80-kWh battery would cost about $24.00 to fully charge (from empty to full) using Level 2, and $32.00 with DC fast charging.
Several apps and online tools will help you locate public charging, including PlugShare’s and Google Maps database.
Incentives and Tax Credits for your EV and EV Charger
If you are in the market for a new vehicle this may be the right time to consider purchasing your first electric vehicle. Currently, Pennsylvania residents are being offered incentives from the state as well as the federal government to help make the switch to fully electric or gas-saving hybrid cars. The rebates and tax breaks may also apply to the purchase of an EV charger and for the EV charger installation. You could also be given another financial break by your utility company if you recharge your car at night.
Property owners that install public commercial charging stations may be eligible for rebates. Electric car charging can attract more traffic to your business, improve tenant or employee satisfaction and retention, and generate a new revenue stream.
Pennsylvania offers rebates on Electric Vehicles and Home & Business Charging Stations.
Click below for more informations.
The Federal Government has tax rebates available.
Below are links to the IRS website with instructions and forms to submit with annual tax return.



